Endosonography, endouzy
- What is endosonography of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum for?
- Why do endosonography of the lower intestine?
- How to prepare for endosonography?
- How is endosonography done?
- How safe is the procedure?
- Bibliography:
 Head of Endoscopy, PhD, surgeon Mikhail Sergeevich Burdyukov talks about minimally invasive endoscopic interventions in the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, and the tracheobronchial tree.
Head of Endoscopy, PhD, surgeon Mikhail Sergeevich Burdyukov talks about minimally invasive endoscopic interventions in the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, and the tracheobronchial tree.
Endosonography in the state of drug sleep on the equipment of expert class Olympus
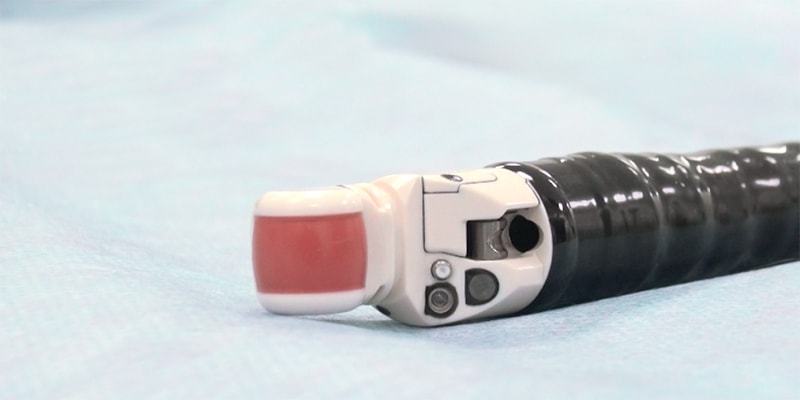
Endosonography is a diagnostic technique that combines the capabilities of ultrasound and endoscopy. For the study using a flexible endoscope with a video camera and an ultrasonic sensor. It can be inserted into the esophagus, stomach, duodenal ulcer, rectum, large intestine, into the respiratory tract.
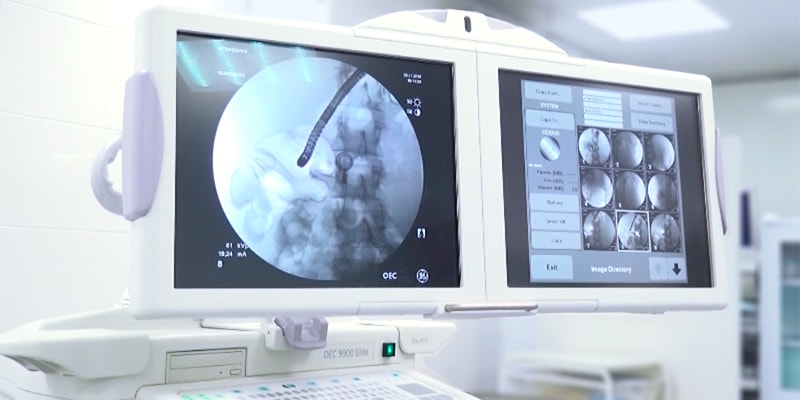
During a routine ultrasound examination through the skin, when you need to examine an organ that is deep, image clarity suffers. Endosonography solves this problem. With the help of an endoscope, the ultrasound sensor is brought as close as possible to the formation being studied.
Endosonography, like conventional ultrasound, can be combined with Doppler sonography to assess blood flow in the vessels. During the study, the doctor may conduct a fine needle biopsy of the suspicious formation.
<Endosonography is of great importance in oncology. It provides an opportunity to establish the stage of the tumor before surgery. This helps the surgeon to choose the optimal tactics and significantly improve the results of treatment.
What is endosonography of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum for?
- Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. The method is highly sensitive and allows you to establish the diagnosis in 90-95% of cases.
- Diagnosis of cancer of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum.
- Identification of benign formations of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Identification, examination and biopsy of focal lesions of the upper GI tract.
- Identification of the cause of abdominal pain, when with the help of other studies can not establish the diagnosis.
- Detection of pathological formations in the gallbladder and biliary ducts, pancreatic duct.
- Biopsy of suspicious formations in the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, adjacent organs, lymph nodes.
- Specification of the degree of expansion of the veins of the esophagus.

Why do endosonography of the lower intestine?
- Diagnosis of cancer of the colon and rectum.
- Biopsy of suspicious formations in the intestine, lymph nodes.
- Assessment of the integrity of the anal sphincter.
- Identification of causes of fecal incontinence.
What is the endosonography of the chest?
- Diagnosis of lung cancer and bronchus.
- Assessment of the status of intrathoracic lymph nodes.
An endoscope with an ultrasound probe is inserted into the esophagus or into the airways (in the latter case, the study is called endobronchial ultrasound ).

How to prepare for endosonography?
Before the examination, the doctor finds out if the patient is allergic to medications, if he suffers from chronic diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory system, diabetes, or if he takes any medications.
If a fine-needle biopsy is planned, blood clotting tests will be required.
A few hours before the study can not eat and drink. Cleansing enemas, laxatives can be prescribed. More detailed recommendations will give a doctor.
Going to endosonography, you need to take someone close to you. When a patient leaves the clinic, he is still under the influence of medication and needs to be accompanied.
How is endosonography done?
Endosonography of the upper gastrointestinal tract resembles gastroscopy , lower parts - sigmoscopy, colonoscopy . The procedure lasts from 30 to 90 minutes. It takes longer when it is supplemented with a fine needle biopsy.
Usually endosonography is carried out in a state of drug sleep - a kind of light anesthesia. In this state, during the procedure, the patient feels almost nothing, can feel only slight discomfort. During endosonography, the doctor monitors the patient's blood pressure, pulse, oxygen level in the blood.
About an hour later, the doctor allows you to get up, and if the patient’s condition is in order, she lets go home. On this day, you can not get behind the wheel and do work that requires concentration.
How safe is the procedure?
Like any endoscopic examination, endosonography is associated with certain risks, but they are extremely low - about 1 case per 2000 studies.
You need to consult a doctor if, after endosonography, the following symptoms bother you:
- severe pain;
- nausea, vomiting (especially with blood);
- chills, fever
Bibliography:
- Ways to improve the efficiency of fine-needle punctures under the control of endosonography: a retrospective analysis of non-informative conclusions of morphological studies - Burdyukov MS, Nechipay AM, Kudryavitsky E.E. 2017 / Volga Cancer Journal
- Endoscopic transgastric neurolysis of the celiac plexus: variants of the effect in chronic pain syndrome in the upper abdomen
Burdyukov M.S., Yurichev I.N., Nechipay A.M. 2016 / Volga Cancer Journal - Fine needle puncture under the control of endoscopic ultrasonography and alternative biopsy methods
Burdyukov MS, Yurichev I.N., Nechipai A.M. 2012 / Experimental and clinical gastroenterology - Endobronchial ultrasonography of the mediastinum and broncho-pulmonary system
Korolev V.N., Burdyukov M.S., Surovtsev I.Yu., E.A. Sazhina, 2016 UDC 616.24-006-072 2016 / Volga Volgograd Oncological Herald
Record on consultation around the clock
What is endosonography of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum for?Why do endosonography of the lower intestine?
How to prepare for endosonography?
How is endosonography done?
How safe is the procedure?
What is endosonography of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum for?
Why do endosonography of the lower intestine?
What is the endosonography of the chest?
How to prepare for endosonography?
How is endosonography done?