What is the listener at the doctor. Order a medical device for listening to breathing
- Types of instruments to listen to the breath
- Where to buy a stethoscope in Moscow?
- Stethoscope and phonendoscope. Story
- Stethoscope and phonendoscope what is the difference
Medical device used for listening internal organs person, in order to determine the noise in them is called a stethoscope. You can meet him not only with a general practitioner. Stethoscope and listen to the bronchi, and lungs, and intestines, blood vessels.
The history of this device began in 1816, when it was invented by a French doctor and scientist Rene Laennec. After some time, another device based on this was invented - the phonendoscope, which today has become popular with general practitioners. Both types of stethoscopes are in demand and have taken a worthy place in medical practice. A stethoscope is most often made of wood, but there are also aluminum variations.
In the modern world, a stethoscope has another look. The device of this medical device is not complicated: ear tips, a head that is applied to the patient's body and a tube connecting the two elements listed above and conducting a sound.
Today in the market of medical equipment there is a fairly large variety of stethoscopes, allowing to obtain accurate data on the work of the human body.
An obstetric stethoscope allows you to hear the fetal heartbeat.
Pediatric stethoscope is great for listening to light children, as it has excellent acoustics. The main advantage of this model is that the bezel does not cause a feeling of cold.
Electronic stethoscope - it differs from the usual model in that it comes with a headset and a microphone. More and more professionals prefer this particular model. Combined in an electronic stethoscope, advances in medical technology make it possible to listen to a patient in noisy rooms while suppressing external noises.
Cardiac stethoscopes are used in cardiology, allowing the attending physician to listen to high and low frequencies.
Like every medical equipment, a stethoscope requires proper storage and use.
Rule 1 - listening to the lungs or other organs should be carried out in a bright warm room to avoid extraneous noise and irritants that can cause the patient to react.
Rule 2 - for listening with a stethoscope, the patient should be stripped.
Rule 3 - the doctor should be able to examine the patient from different angles. And in different positions (sitting, standing, lying). Examination of the patient from the right side reduces the possibility of hitting extraneous noise, which guarantees the quality of the examination.
Rule 4 - a stethoscope must have a funnel mode and a diaphragm mode, for listening to bass and treble.
Rule 5 - the main thing is to comply with all listening points so that the data are reliable.
There are several listening points:
The point of listening to the valves of the pulmonary artery is located at the left edge of the sternum at the second intercostal space;
The point of listening to the mouth of the aorta and aortic valves is located at the right edge of the sternum at the second intercostal space;
The point of listening of the tricuspid valve is located at the left edge of the sternum of the IV intercostal space;
The point of listening of the left atrioventricular orifice and mitral valve = apex of the heart is the fifth intercostal space along the mid-key line.
Buy a stethoscope today is not difficult, because quite a lot, both domestic and foreign manufacturing companies today are represented on our market. Popular manufacturers are companies from Germany - Duplex, KaWe, Dimeda Instrumente, from the USA - Littmann, from the UK - Medicare and from Singapore - Little Doctor.
04/05/2014
The stethoscope (a device for listening to the noise of internal organs) was invented in 1816 by a modest French doctor named René Theophile Hyacinth Laennec. (Laennec Rene Theophile Hyacinthe), one of the founders of the modern clinic of internal diseases, Napoleon I’s personal physician
The exact circumstances of the invention are unknown. But after the death of Laennec it was rumored that he invented the stethoscope due to its gallantry. So, in 1816, Rene Laennec was once again summoned to a patient suffering from tuberculosis, who, we note, was a beautiful young woman. At the same time, the piquancy of the situation consisted in the fact that the doctor who came for the examination encountered difficulty in percussion (tapping certain parts of the body and analyzing the arising sound phenomena) due to the large size of the patient's mammary glands - to perform a direct auscultation of the lungs, i.e., attach the ear to the bare Breast examined was, according to Laenneck, "unacceptable" due to the young age and sex of the girl.
In order to adequately get out of the current predicament, the young doctor, on reflection, undertook something new. He recalled how a few days ago, walking through the Tuileries Garden in Paris, he saw children scratching a wooden cane with a pin at one end and listening to the sounds that arose at the other. Deciding that with the help of this method it is possible to listen to the noises emanating from the chest, inspired by Laennec boldly rolled a piece of paper (sheet music) into a tube and applied it to the patient's chest. To his surprise, he managed to still hear respiratory noise the patient, and without even touching her, which the doctor Laennec wanted, repeated this experience on his patients. He made sure that the air column in the tube enhances the sounds coming from the body, ordered the carpenter several wooden tubes of different widths and began to experiment with them. He found that the width of the tube does not affect the intensity of the sound. However, the audibility increased depending on the length of the tube. Experienced Laennec determined the optimal tube size and created the world's first stethoscope - a device for listening to patients.

It should be noted that auscultation of the lungs, as a method of physical diagnosis, has existed since ancient times. He was mentioned in the works of Hippocrates, who, teaching the doctors of his time, advised them to directly apply their ear to the rib cage and listen to medically important noises.
On the basis of the invented stethoscope, Laennec developed and introduced auscultation into medical practice - a method of examining internal organs by listening to the sound phenomena that they reproduce. The method was presented in full in his famous work on direct auscultation “De l'auscultation mediate, ou Traite du diagnostic des maladies du poumon et du coeur, fonde principalement sur ce nouveau moyen dʻexploration”, presented by the French Academy of Medicine in 1819. Many of the auscultatory phenomena described by Laennec are still used today: egophony, metallic chime, noise (amphoraic, blows, terpuga, saws, inflated furs, etc.), pueril respiration, saccadian breathing, percussion percussion, pectorylovisis, etc. .
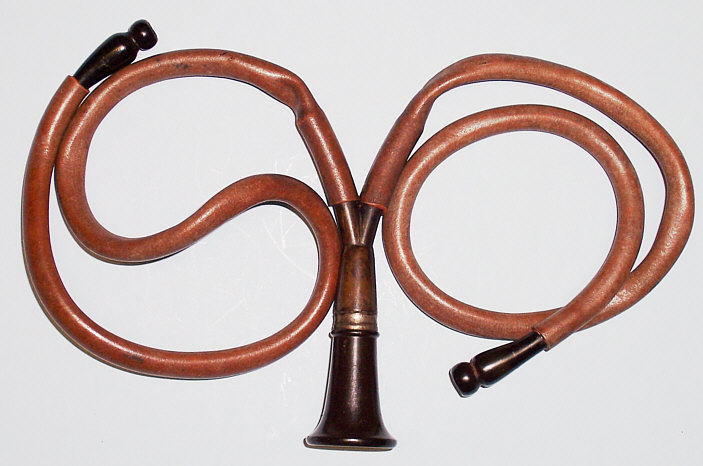

It must be said that the stethoscope later underwent a number of changes, its device was improved, but the principle of operation and the physics of the device remained unchanged. Later, the phonendoscope was also invented (the name was invented by Nikolai Sergeevich Korotkov - a scientist who discovered the method of measuring blood pressure ), having in its construction a tensioned membrane, which significantly enhances the volume of the sound.
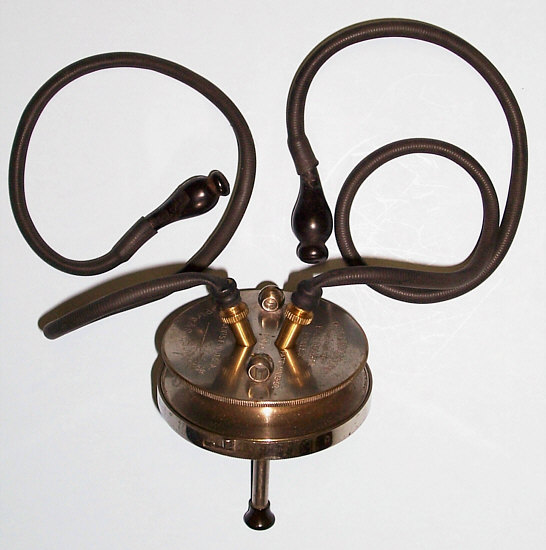

At the same time, at present, the most popular among medical workers is the combined version (“two in one”) of the stethoscope and the phonendoscope - the stethophonendoscope. The peculiarity and advantage of such a hybrid device is that at one end it has a phonendoscope tip with a membrane, and on the other - a stethoscope tip without a membrane. In conclusion, I would like to note that, from a practical point of view, it is advisable to use a stethoscope for auscultation of the cardiovascular system, since low-frequency sounds are better carried out in the absence of a membrane and low pressure on the skin. During auscultation of the lungs, it is better to listen with a phonendoscope, since high-frequency sounds are better carried out using a membrane.
To listen to the work of the internal organs of a person, use a special device - a stethoscope. With it, organs such as lungs, bronchi, intestines are bugged. A medical device for listening to breathing, the price of which is quite affordable, was invented in the early 19th century. In addition to the stethoscope, another similar device is used - the phonendoscope. The difference between them is that the first is used to listen to low heart or intestinal frequencies, and the second - the high frequencies of blood vessels or lungs.
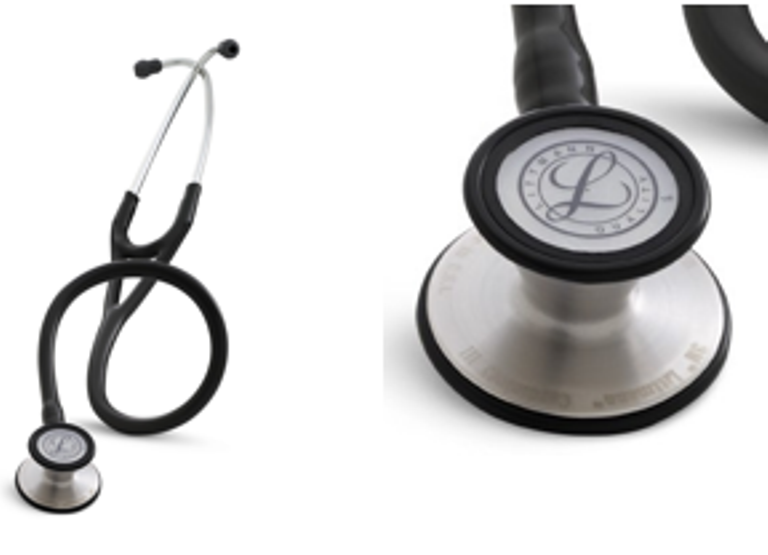
A stethoscope consists of the following parts:
- Head applied to the body.
- The sound duct is a hose that conducts sound from the head.
- The arms are metal tubes adjacent to the doctor's ears.
- Olives - nozzles at the ends of the bows.
The head of a stethoscope can be plastic, steel or aluminum. The preferred option is a steel head. It is better to choose a thicker vinyl conduit, rather than rubber. More comfortable are the soft rubber olives, which adapt to the shape of the ears. It is also recommended to order medical device for listening to breathing with a metal spring, tightening the arms.
Types of instruments to listen to the breath
Stethoscopes and phonendoscopes are actively used by doctors of many specialties, such as, pediatrics, pulmonology, emergency workers and even veterinarians. The reason for such a wide distribution is the ease of use and the great possibilities of obtaining information from the sounds of a person’s breath. In Moscow, separate devices are used to listen to the breathing of small children, adults and pregnant women.
You can order the following medical device for listening to breathing: 
- Therapeutic.
- Neonatal.
- Pediatric.
- Rappaport stethoscope.
- Cardiological.
- Obstetric.
- Electronic.
All of the above types of stethoscopes are used in specific cases, but there are also universal models. For example, Rappaport's stethoscope is used for auscultation of adults and children. It is quite heavy, as it has 2 sound ducts and the ability to install different membranes and funnels. The electronic stethoscope is different from other devices, as it has a built-in microphone that converts breath sounds into electronic signals. Before entering the olives, these signals are processed again. Phonendoscopes are used only binaural, consisting of 2 tubes.
Where to buy a stethoscope in Moscow?

Listening to the patient's breathing is a quick and informative procedure that many doctors perform. If you need a stethoscope or phonendoscope in Moscow, please contact the company "". We sell only high quality at an affordable price from world-famous manufacturers.
Stethoscope and phonendoscope. Story
Yeah! Once they do not call what the doctor puts to the chest or back of the patient - a stethoscope, a phonendoscope or a stethophonendoscope. But the mechanical tonometer. What we listen to the brachial artery? Stethoscope or phonendoscope? It is written: “Tonometer with a built-in stethoscope” - so, there is no difference?
And the difference is.
And there is a fascinating story about Napoleon Bonaparte's doctor - Rene Laenneke, who in 1816 because of his internal delicacy could not put his ear to the chest of a sick young girl, and, to spare her modesty, began to listen to the heart and lungs. About a miracle - the sounds were stronger. Thus was born the stethoscope - from the Greek words stethos - chest, and skopeo - I observe.
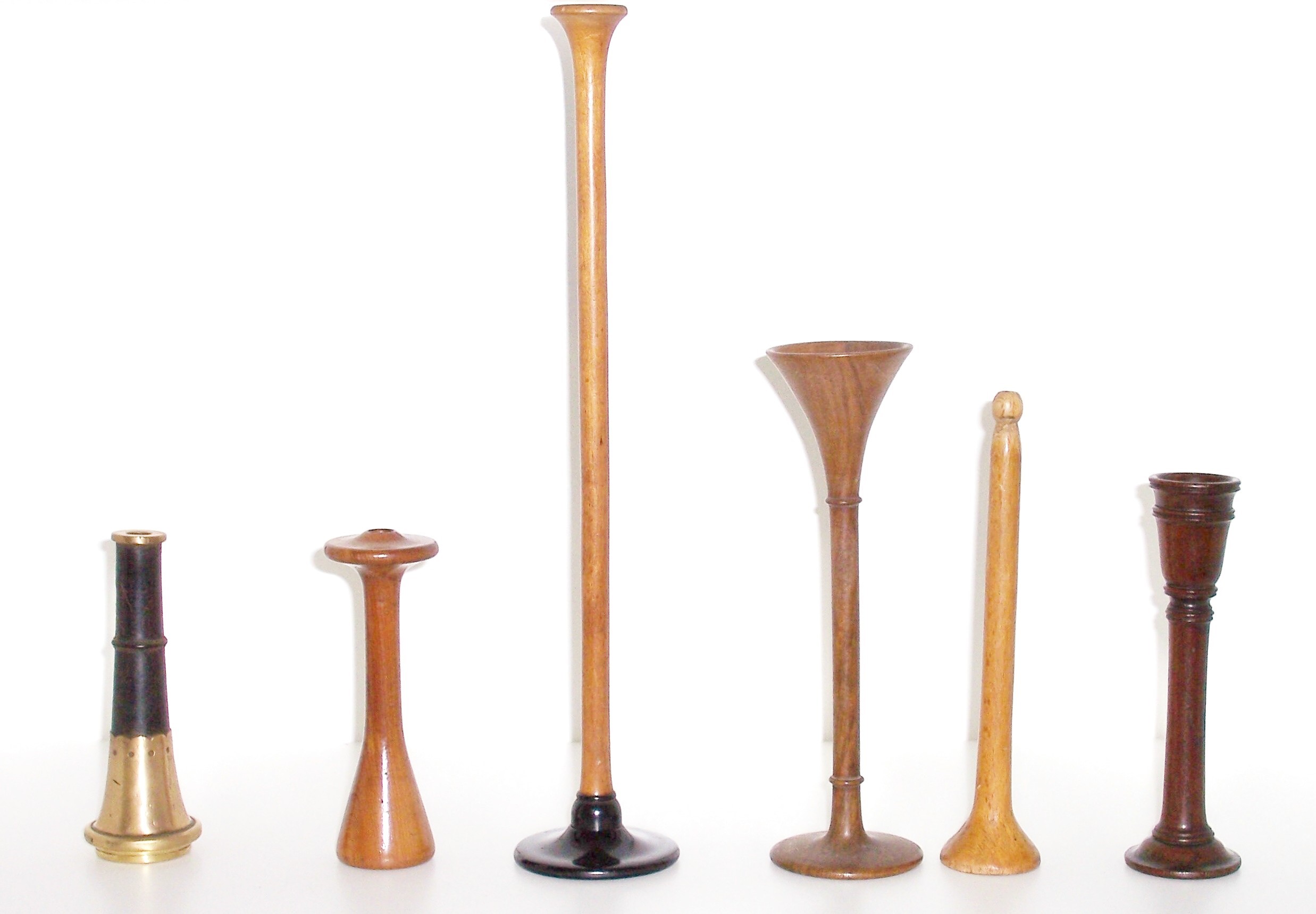

And only at the beginning of the 20th century - almost 100 years later, the Russian surgeon Nikolai Sergeevich Korotkov (it was he who invented the auscultatory method for measuring pressure), improved it by pulling the membrane on the socket - and called this instrument the phonendoscope.
Stethoscope and phonendoscope what is the difference
What is the difference between a stethoscope and a stethoscope?
Mainly high-frequency sounds (light, vessels) pass through the membrane of the phonendoscope, and low-frequency sounds (heart, intestines) pass through the funnel: the bottoms as if muffle high-frequency vibrations.
The membrane of the stethoscope significantly reduces the volume of the entire sound and the bottoms become very quiet. At the same time, high frequencies are clearly audible.
As you can see the difference between a stethoscope and a phonendoscope with the scope of application: With the phonendoscope membrane, we listen to the high tones of the lungs and blood vessels, and the stethoscope's bell with low frequencies of the heart or bowel.
The difference between a stethoscope and a phonendoscope is visible to the naked eye.



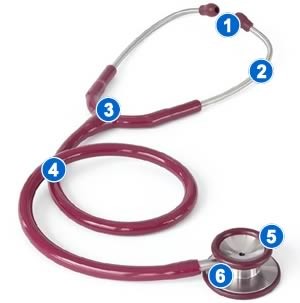
5 and 6 - Head of stetofonendoskop
A stetofonendoskop consists of a head: on one side there is a bell (5), and on the other, a membrane (6), a conductive tube (4), a tee (3), headband springs (a metal plate connecting the headband tubes. There is no figure in it ), headbands (2) with olives (1).
The acoustic data of a stethoscope depend on the internal shape and design of the head used by the manufacturers.
What you need to know about stethoscopes and phonendoscopes
The price of a good stetofendoskop varies from 90 to 200 dollars. Lower price indicates lower quality.
About the design: The material of the head can be different - plastic, aluminum or stainless steel. The best material is a well-finished stainless steel. It is important that the stethoscope fits snugly to the patient's body and air does not get in there - any leakage of air leads to a loss of sound transmission.
The diaphragm, or diaphragm, must be flexible, durable and fit snugly to the body.

The connecting tube of the stethoscope the thicker the better. Moreover, vinyl tubes are better than rubber isolate external noise.
Studies have shown that the ideal length of the stetofonendoscope tube is 30 cm with an opening diameter of 4.6 mm. But on sale, we see lower-quality sound, but more comfortable tubes, 50-55 cm long.
Compromise tube length 37.5 cm
Tips headband (or olive) are hard plastic and soft rubber or helium. The latter, of course, are better, since they are attached to the shape of the user's ear canal.
Metal tube headband can be connected with a metal spring, which, of course, improves usability.
The head of stethoscopes can be single, double (bell / membrane), double membrane (large diameter / small), double with a grooved head
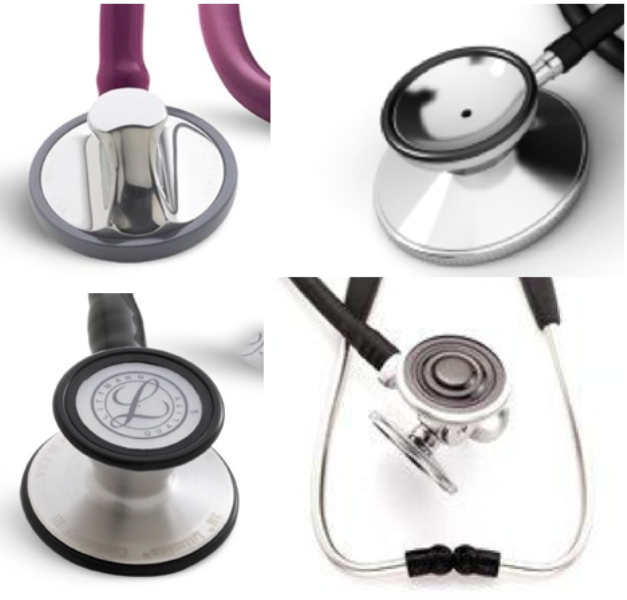

Currently, Littmann invented heads with a tunable or dual-frequency membrane: To hear low frequencies (bell mode), lightly attach the acoustic head to the patient.
To listen to high frequencies you need to tightly press the head: the movement of the diaphragm membrane becomes limited. Low-frequency sounds are blocked, and high-frequency noises are heard
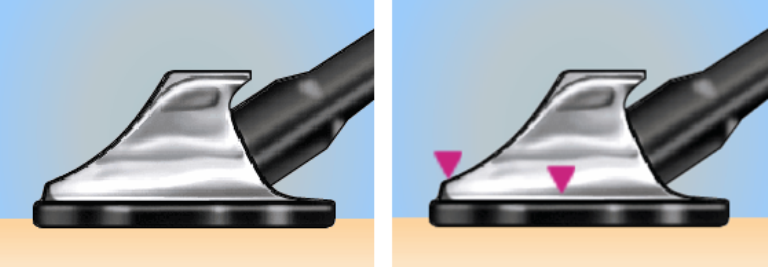
Littmann stethoscopes can have two adjustable diaphragms - large for adults and small for children.
In addition, there are stethophonendoscopes for infants and young children, as well as fetal stethoscopes for pregnant women to listen to the fetus.
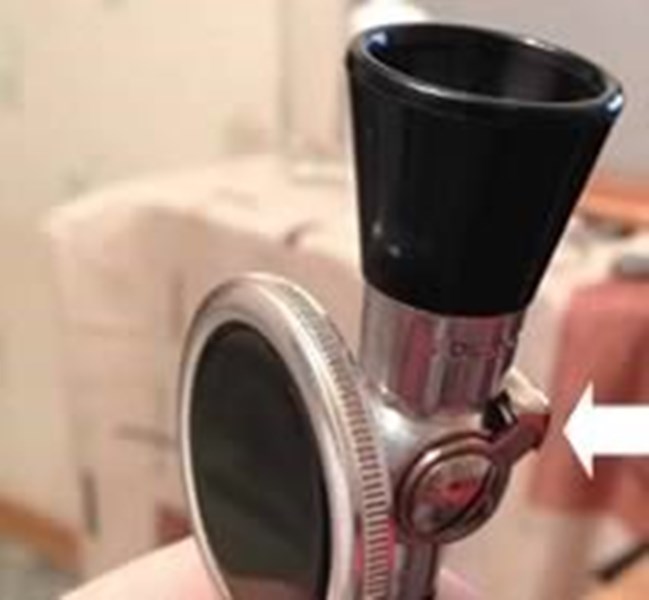

At present, the stethoscope endoscope is the classic version of a stethoscope, which combines in its two-sided head a funnel (like a stethoscope) and a membrane (like a phonendoscope). In general, phonendoscopes and stethophonendoscopes are called the term “stethoscope”.
Where to buy a stethoscope in Moscow?What we listen to the brachial artery?
Stethoscope or phonendoscope?
It is written: “Tonometer with a built-in stethoscope” - so, there is no difference?